The movement of people across borders, known as immigration, has shaped the course of human history. Throughout time, individuals and communities have migrated in search of better opportunities, safety, or simply a new beginning. In recent decades, globalization and technological advancements have accelerated the pace of migration, leading to complex and ever-changing immigration trends.
This comprehensive analysis delves into the multifaceted world of immigration, examining historical patterns, driving factors, and the impact on both sending and receiving countries. We will explore the demographics of immigrants, their motivations, and the challenges and opportunities they face in integrating into new societies.
By understanding these trends, we can better inform policy decisions and foster a more inclusive and equitable global community.
Global Migration Patterns
Throughout history, humans have migrated across the globe in search of better opportunities, safety, and a better life. These movements have shaped the demographics and cultures of nations, leaving a lasting impact on the world.
Factors Driving Migration
The decision to migrate is often influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including:
- Economic factors: Poverty, unemployment, and the search for better economic opportunities are major drivers of migration.
- Political factors: War, persecution, political instability, and human rights violations force many people to flee their home countries.
- Environmental factors: Natural disasters, climate change, and environmental degradation can displace populations and lead to migration.
Migration Statistics
According to the United Nations, the number of international migrants has grown steadily over the past decades, reaching 281 million in 2020. This represents 3.6% of the world’s population.
- The top countries of origin for international migrants are India, Mexico, China, Russia, and Bangladesh.
- The top destination countries for international migrants are the United States, Germany, Saudi Arabia, Russia, and the United Kingdom.
Immigration Trends
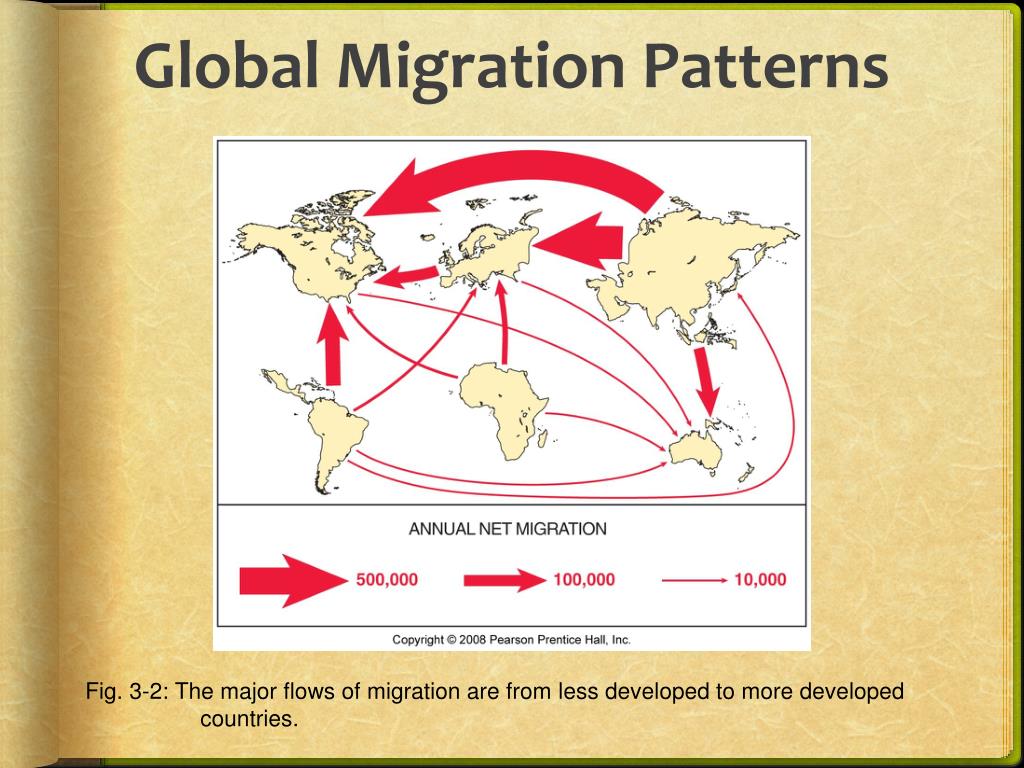
Immigration has become an increasingly prevalent phenomenon worldwide, shaping the demographics and economies of nations. Understanding the major immigration corridors, demographics, motivations, and experiences of immigrants provides valuable insights into global migration patterns.
Major Immigration Corridors and Destinations
Major immigration corridors connect regions with significant economic disparities, political instability, or environmental challenges. Prominent corridors include:
- Mexico to the United States
- India to the Gulf Cooperation Council countries
- China to Southeast Asia
- Sub-Saharan Africa to Europe
Key destinations for immigrants include the United States, the European Union, Canada, Australia, and the Gulf Cooperation Council countries.
Demographics of Immigrants
Immigrants come from diverse backgrounds and demographics. Common characteristics include:
- Age: Typically between 25 and 44 years old, seeking better economic opportunities and stability.
- Gender: Historically male-dominated, but increasingly balanced in recent years.
- Education Levels: Vary widely, from low to high levels of education and skills.
Motivations and Experiences of Immigrants
The motivations for immigration are complex and multifaceted. Common reasons include:
- Economic Factors: Seeking better employment opportunities, higher wages, and improved living standards.
- Political Factors: Fleeing persecution, conflict, or authoritarian regimes.
- Environmental Factors: Escaping natural disasters, climate change, or environmental degradation.
- Social Factors: Reuniting with family, pursuing education, or seeking a better quality of life.
Immigrants often face challenges upon arrival, such as language barriers, cultural differences, and discrimination. However, many also contribute significantly to their new societies through their skills, knowledge, and cultural perspectives.
Economic Impact of Immigration
Immigration significantly influences labor markets, wages, and economic growth. The influx of immigrants can affect the supply and demand for labor, potentially altering wages and employment opportunities for native-born workers.
Labor Market Impact
The impact of immigration on the labor market is complex and depends on factors such as the skill level of immigrants, the size of the immigration flow, and the overall economic conditions. In general, the influx of low-skilled immigrants can increase the supply of labor, potentially leading to lower wages for low-skilled native-born workers.
Conversely, the arrival of high-skilled immigrants may increase competition for high-skilled jobs and drive up wages in certain sectors.
Wage Effects
The wage effects of immigration vary widely across studies. Some research suggests that immigration can have a small negative impact on the wages of low-skilled native-born workers, particularly in industries with a high concentration of immigrant workers. However, other studies find that the impact is negligible or even positive, as immigrants often create new jobs and contribute to economic growth.
Economic Growth
Immigration can contribute to economic growth by increasing the labor force, fostering innovation, and expanding consumer markets. Immigrants often bring new skills and ideas that can boost productivity and lead to the creation of new businesses. Additionally, immigrants can increase demand for goods and services, stimulating economic activity.
Potential Benefits and Challenges
Immigration can bring both benefits and challenges to host countries.
Benefits
- Increased labor force and economic growth
- Innovation and entrepreneurship
- Cultural diversity and exchange
Challenges
- Potential for wage suppression in low-skilled sectors
- Competition for housing and other resources
- Social and cultural tensions
Examples of Immigration Policies
Successful immigration policies often focus on integrating immigrants into the host society while balancing economic needs with social concerns.
Successful Policies
- Canada’s points-based system, which selects immigrants based on their skills and education
- Australia’s skilled migration program, which targets workers in high-demand occupations
Unsuccessful Policies
- Uncontrolled mass migration, which can lead to social and economic problems
- Restrictive immigration policies, which can hinder economic growth and innovation
Social and Cultural Impact of Immigration
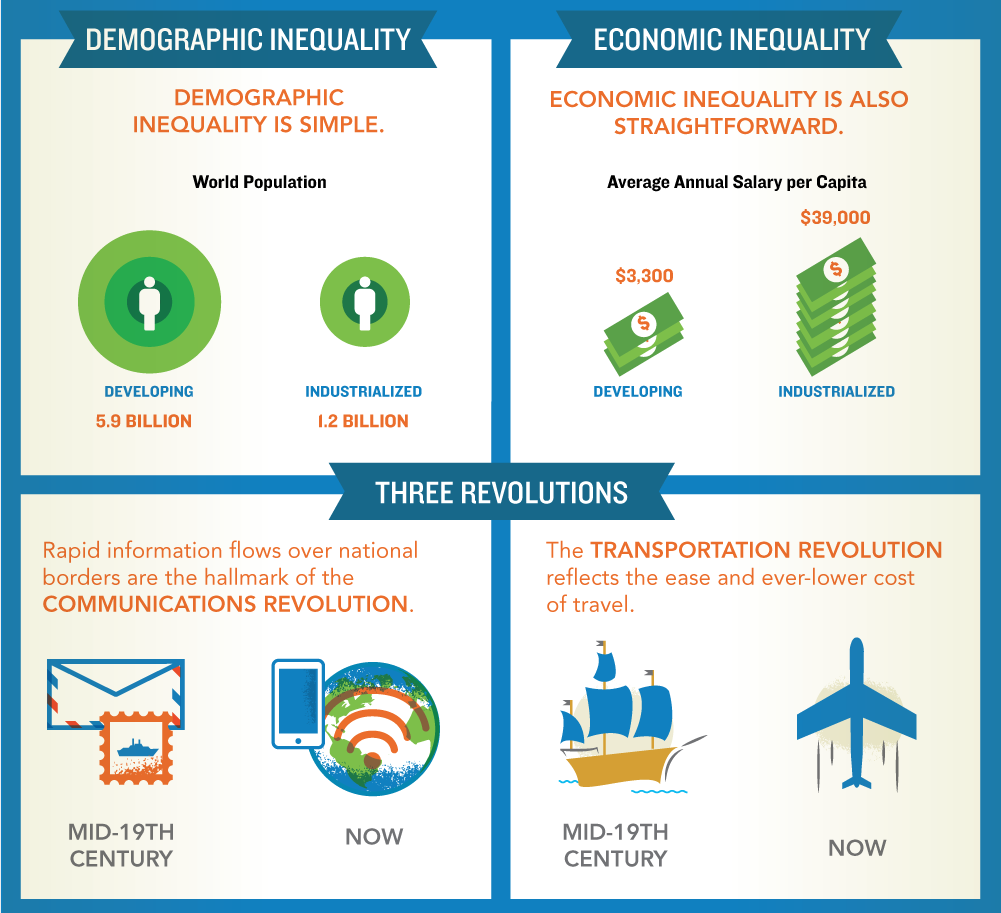
Immigration has profound social and cultural implications, affecting social cohesion, cultural diversity, and national identity. Integrating immigrants into new societies presents both challenges and opportunities.
Social Cohesion
Immigration can impact social cohesion in complex ways. On one hand, it can foster diversity and create new cultural connections. On the other hand, it can sometimes lead to social tensions and conflicts, particularly if immigrants are perceived as a threat to the dominant culture or job market.
Successful integration policies prioritize creating a welcoming environment, promoting civic engagement, and providing support services to help immigrants adapt to their new communities.
Cultural Diversity
Immigration contributes significantly to cultural diversity, introducing new languages, traditions, and perspectives into host societies. This can enrich cultural landscapes and promote greater understanding and appreciation of different cultures.
However, cultural diversity can also pose challenges, such as language barriers, cultural misunderstandings, and potential clashes between different value systems. Successful integration policies strive to balance the preservation of cultural heritage with the promotion of inclusivity and mutual respect.
National Identity
Immigration can influence national identity in various ways. It can reshape the demographic makeup of a society, introducing new ethnicities and cultural influences. This can lead to both a re-evaluation of national identity and a sense of shared belonging among diverse populations.
Successful integration policies aim to foster a sense of shared purpose and belonging, while recognizing and valuing the contributions of immigrants to the nation’s cultural and economic fabric.
Future Trends in Immigration
As global interconnectedness and technological advancements continue to shape our world, the future of immigration patterns remains a subject of great interest. Predicting these trends is complex, influenced by a multitude of factors that will shape human mobility in the years to come.
Climate change, for instance, is expected to exacerbate environmental degradation and natural disasters, potentially displacing millions of people from their homes. Technological advancements, such as improved transportation and communication, may facilitate migration by reducing barriers and costs associated with relocation.
Policy Recommendations
- Develop comprehensive and forward-looking immigration policies that anticipate future trends and address emerging challenges.
- Invest in research and data collection to better understand the causes and consequences of migration, informing policy decisions.
- Promote international cooperation to address the root causes of displacement, such as poverty, conflict, and environmental degradation.
- Support integration programs and policies that foster the successful integration of immigrants into their new communities.
Outcome Summary
As the world continues to grapple with the complexities of migration, it is imperative that we approach this issue with empathy, understanding, and a commitment to finding sustainable solutions. By fostering dialogue, promoting cooperation, and implementing evidence-based policies, we can harness the transformative power of immigration to build thriving and inclusive societies for all.
Answers to Common Questions
What are the main factors driving migration?
Economic disparities, political instability, environmental disasters, and family reunification are among the primary factors.
How does immigration impact labor markets?
Immigration can both complement and compete with the native workforce, potentially leading to wage adjustments and skills shortages.
What are the challenges of integrating immigrants into new societies?
Language barriers, cultural differences, and discrimination can hinder integration, making it crucial to provide support systems and foster inclusive environments.



