Spinal cord injuries (SCIs) sustained in car accidents can have a profound and lasting impact on an individual’s life. These injuries, which affect the spinal cord and its surrounding structures, can lead to a range of physical, cognitive, and emotional challenges that extend far beyond the initial trauma.
Understanding the long-term implications of SCIs and the essential care required for individuals living with these injuries is crucial for ensuring their well-being and maximizing their quality of life.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the different types of SCIs, their causes, and the various treatment and management strategies available. We will also delve into the physical, cognitive, and emotional effects of SCIs, examining how they can impact mobility, daily functioning, and overall well-being.
Additionally, we will discuss the social and economic implications of SCIs, highlighting the challenges individuals may face in employment, relationships, and accessing essential resources.
Introduction

Spinal cord injuries (SCIs) are a serious consequence of car accidents, often resulting in life-changing disabilities. In the United States alone, approximately 17,000 new cases of SCI occur each year, with car accidents accounting for nearly half of these injuries.
SCIs can have a profound impact on an individual’s physical, cognitive, and emotional well-being. The severity of the injury can range from minor, causing temporary pain and numbness, to severe, resulting in paralysis and loss of sensation below the level of the injury.
Long-Term Implications
The long-term implications of SCIs can be significant and vary depending on the severity and location of the injury. Physical effects may include paralysis, loss of sensation, muscle weakness, and impaired mobility. Cognitive effects can include difficulty with memory, attention, and problem-solving.
Emotional effects may include depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Types of Spinal Cord Injuries
Spinal cord injuries (SCIs) are categorized based on the extent and location of the damage. Understanding the different types of SCIs is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment and rehabilitation strategies.
SCIs can be classified into two main types:
Complete Injuries
In complete SCIs, the spinal cord is completely severed, resulting in a loss of all motor and sensory function below the level of the injury. Individuals with complete SCIs may experience paralysis, loss of sensation, and impaired bladder and bowel control.
Incomplete Injuries
Incomplete SCIs occur when the spinal cord is not completely severed, allowing for some degree of function to be preserved. The extent of the remaining function depends on the severity and location of the injury. Incomplete SCIs can be further classified into various levels based on the region of the spinal cord affected.
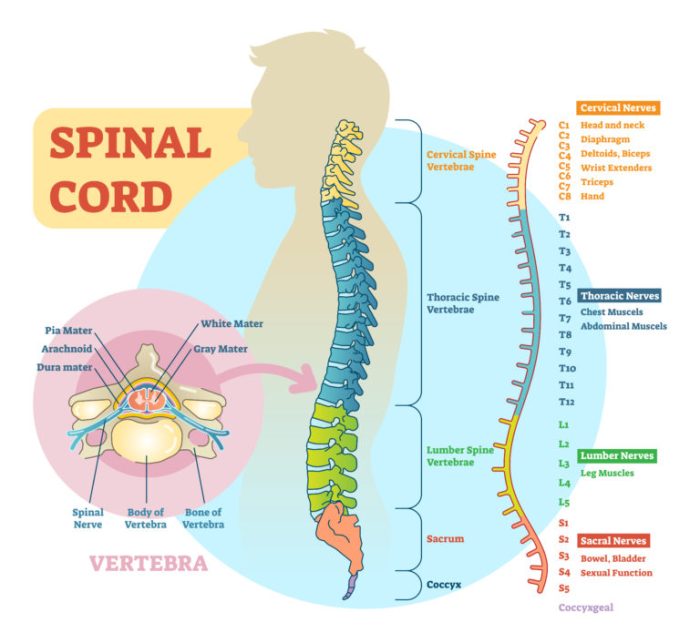
Levels of Spinal Cord Injuries
SCIs are also classified based on the level of the spinal cord affected. The spinal cord is divided into five main regions:
- Cervical (C1-C8): Controls the neck, shoulders, arms, and hands
- Thoracic (T1-T12): Controls the chest, abdomen, and back
- Lumbar (L1-L5): Controls the lower back, legs, and feet
- Sacral (S1-S5): Controls the pelvic organs, bladder, and bowel
- Coccygeal (Co1-Co5): Provides minimal sensation and movement in the tailbone area
The level of the SCI determines the specific functions that are affected. For example, an injury at the cervical level may result in paralysis of the arms and legs, while an injury at the lumbar level may affect only the legs.
Treatment and Management of SCIs
The treatment of spinal cord injuries (SCIs) is complex and requires a multidisciplinary approach involving various healthcare professionals. Treatment options depend on the severity and location of the injury.
Acute Treatment
Acute treatment aims to stabilize the spine and prevent further damage to the spinal cord. It may involve immobilization using a cervical collar or a spinal brace, medication to reduce swelling and pain, and surgery to remove any fragments of bone or other structures that may be pressing on the spinal cord.
Long-Term Treatment
Long-term treatment focuses on maximizing function, improving quality of life, and preventing complications. It includes:
- Rehabilitation: Rehabilitation is crucial for improving function and quality of life after an SCI. It involves physical therapy to improve mobility and strength, occupational therapy to enhance daily living skills, and speech therapy to address communication difficulties.
- Medications: Medications can be used to manage pain, spasticity, and other symptoms associated with SCIs.
- Assistive devices: Assistive devices such as wheelchairs, walkers, and canes can help individuals with SCIs regain mobility and independence.
- Counseling and support: Counseling and support groups can provide emotional support and guidance to individuals with SCIs and their families.
Physical Effects of SCIs
Spinal cord injuries (SCIs) can have a profound impact on an individual’s physical well-being, resulting in a range of impairments that affect mobility, daily activities, and independence. These physical effects can manifest in various forms, including paralysis, sensory loss, and pain.Paralysis
is a common consequence of SCIs, occurring when the spinal cord is damaged and the brain can no longer send signals to the muscles below the injury site. This can result in partial or complete loss of motor function, affecting the ability to move limbs, control bowel and bladder function, and engage in other physical activities.Sensory
loss is another significant physical effect of SCIs. Damage to the spinal cord can disrupt the transmission of sensory information from the body to the brain, leading to a loss of sensation in the affected areas. This can manifest as numbness, tingling, or complete loss of feeling in the limbs, trunk, or other parts of the body.Pain
is a prevalent issue for individuals with SCIs. The damage to the spinal cord can cause chronic pain, which can be debilitating and interfere with daily life. The pain can range from mild to severe and may be neuropathic, musculoskeletal, or radicular in nature.
Cognitive and Emotional Effects of SCIs
Spinal cord injuries (SCIs) can have profound cognitive and emotional effects on individuals. These effects can range from mild to severe and can significantly impact a person’s quality of life.SCIs can lead to a variety of cognitive impairments, including difficulties with attention, memory, and problem-solving.
These impairments can make it difficult for individuals to perform everyday tasks, such as working, going to school, or managing their finances.SCIs can also lead to emotional difficulties, such as depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). These difficulties can be caused by the physical pain and disability associated with SCIs, as well as the emotional trauma of experiencing a life-changing injury.Adjusting
to life with a SCI can be a challenging process. Individuals may need to learn new ways to perform everyday tasks, such as dressing, bathing, and eating. They may also need to make changes to their work or school environment to accommodate their disability.
The emotional challenges of living with a SCI can also be significant, and individuals may need to seek professional help to cope with these challenges.
Cognitive Impairments
SCIs can damage the spinal cord, which can lead to cognitive impairments. These impairments can affect a variety of cognitive functions, including:
- Attention
- Memory
- Problem-solving
- Executive function
Attention impairments can make it difficult for individuals to focus and concentrate on tasks. Memory impairments can make it difficult for individuals to remember information, such as names, dates, and appointments. Problem-solving impairments can make it difficult for individuals to solve problems and make decisions.
Executive function impairments can make it difficult for individuals to plan, organize, and carry out tasks.The severity of cognitive impairments can vary depending on the location and severity of the SCI. Individuals with more severe SCIs are more likely to experience cognitive impairments.
Emotional Difficulties
SCIs can also lead to a variety of emotional difficulties, including:
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
Depression is a common emotional difficulty experienced by individuals with SCIs. Depression can cause feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and worthlessness. Anxiety is another common emotional difficulty experienced by individuals with SCIs. Anxiety can cause feelings of worry, fear, and panic.
PTSD is a mental health condition that can develop after experiencing a traumatic event, such as a SCI. PTSD can cause flashbacks, nightmares, and avoidance of reminders of the traumatic event.The emotional difficulties associated with SCIs can be significant and can interfere with an individual’s quality of life.
Individuals who experience emotional difficulties should seek professional help to cope with these challenges.
Adjusting to Life with a SCI
Adjusting to life with a SCI can be a challenging process. Individuals may need to learn new ways to perform everyday tasks, such as dressing, bathing, and eating. They may also need to make changes to their work or school environment to accommodate their disability.The
emotional challenges of living with a SCI can also be significant. Individuals may experience feelings of grief, loss, and anger. They may also feel isolated and alone. It is important for individuals with SCIs to seek support from family, friends, and other individuals who understand what they are going through.
Social and Economic Implications of SCIs
Spinal cord injuries (SCIs) have far-reaching social and economic consequences that can profoundly impact individuals and their families.Employment is a significant concern for individuals with SCIs. Physical limitations, cognitive impairments, and discrimination can make it challenging to secure and maintain gainful employment.
As a result, individuals with SCIs often experience higher rates of unemployment and underemployment compared to the general population.Relationships can also be affected by SCIs. Physical challenges, changes in body image, and emotional difficulties can strain relationships with family members, friends, and romantic partners.
Individuals with SCIs may experience social isolation, loneliness, and a diminished quality of life.Financial burdens are another major challenge for individuals with SCIs. Medical expenses, rehabilitation costs, and assistive devices can place a significant financial strain on individuals and their families.
Additionally, reduced earning potential due to unemployment or underemployment can further exacerbate financial difficulties.Accessing healthcare, education, and other resources can also be challenging for individuals with SCIs. Physical barriers, transportation difficulties, and lack of accessibility can make it difficult to attend appointments, pursue education, or participate in community activities.
Healthcare Access
Individuals with SCIs often require ongoing medical care, including specialized treatments, rehabilitation, and pain management. However, access to these services can be limited due to a lack of insurance coverage, high out-of-pocket costs, and transportation challenges.
Education Access
Education is crucial for individuals with SCIs to achieve their full potential and participate in society. However, physical barriers, transportation difficulties, and lack of accommodations can make it challenging for individuals with SCIs to attend school or university.
Social Participation
Social participation is essential for well-being and quality of life. However, individuals with SCIs may face barriers to social participation due to physical limitations, transportation difficulties, and social stigma.Addressing the social and economic implications of SCIs is crucial to improving the lives of individuals with SCIs and their families.
This includes providing accessible healthcare, education, and social services; promoting employment opportunities; and reducing discrimination and stigma.
Care and Support for Individuals with SCIs
Ongoing care and support are crucial for individuals with spinal cord injuries (SCIs) to maintain their health, well-being, and quality of life. This involves a multidisciplinary approach that includes medical interventions, rehabilitation, and social and emotional support.Family, friends, and healthcare professionals play vital roles in providing support to individuals with SCIs.
Family and friends offer emotional support, practical assistance, and encouragement, while healthcare professionals provide medical care, rehabilitation, and guidance on managing the physical and cognitive challenges associated with SCIs.
Role of Family and Friends
Family and friends can provide invaluable support to individuals with SCIs in several ways:
- Emotional support: They can offer love, understanding, and encouragement, helping the individual cope with the emotional challenges of living with a SCI.
- Practical assistance: They can help with daily tasks such as transportation, meal preparation, and personal care, allowing the individual to maintain independence and quality of life.
- Advocacy: They can advocate for the individual’s needs and rights, ensuring they receive appropriate care and support.
Role of Healthcare Professionals
Healthcare professionals play a crucial role in the care and management of individuals with SCIs. They provide medical care, rehabilitation, and guidance on managing the physical and cognitive challenges associated with SCIs.The healthcare team may include:
- Physicians: They diagnose and treat medical complications, prescribe medications, and provide guidance on managing symptoms.
- Rehabilitation specialists: They develop and implement rehabilitation plans to help individuals regain function and improve their quality of life.
- Nurses: They provide nursing care, monitor the individual’s condition, and educate them on self-care and management.
- Psychologists: They provide counseling and support to help individuals cope with the emotional challenges of living with a SCI.
Prevention of Spinal Cord Injuries in Car Accidents
Spinal cord injuries (SCIs) are devastating and can have a profound impact on an individual’s life. Motor vehicle accidents are a leading cause of SCIs, accounting for nearly half of all cases. Understanding the risk factors and implementing preventive measures is crucial to reduce the incidence of these life-altering injuries.
Safe driving practices and the proper use of safety devices are essential in preventing SCIs in car accidents. These include:
Seat Belts
- Seat belts are the most effective way to prevent SCIs in car accidents. They restrain the body during a collision, preventing it from being thrown forward or sideways, which can cause damage to the spinal cord.
- All occupants of a vehicle should wear seat belts, regardless of their seating position.
Airbags
- Airbags are designed to inflate rapidly in the event of a collision, providing a cushion between the occupant and the hard interior of the vehicle.
- Airbags can help to reduce the risk of SCIs by preventing the head and neck from striking the steering wheel, dashboard, or windshield.
Headrests
- Headrests are designed to support the head and neck in the event of a rear-end collision.
- Properly adjusted headrests can help to prevent whiplash, a common cause of SCIs.
Safe Driving Practices
- Obey speed limits and traffic laws.
- Avoid driving under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
- Be aware of your surroundings and anticipate potential hazards.
- Maintain a safe following distance.
- Get regular vehicle maintenance to ensure that all safety features are functioning properly.
Final Thoughts
Living with a spinal cord injury is a complex and ongoing journey that requires a multifaceted approach to care and support. Individuals with SCIs need access to specialized medical care, rehabilitation services, and emotional support to optimize their recovery and achieve their full potential.
By raising awareness about the long-term implications of SCIs and the importance of ongoing care, we can empower individuals living with these injuries to lead fulfilling and independent lives.
FAQ Section
What are the most common causes of spinal cord injuries in car accidents?
The most common causes of spinal cord injuries in car accidents include sudden and forceful impacts, such as those caused by high-speed collisions, rollovers, and rear-end crashes. These impacts can cause the spinal cord to be compressed, stretched, or severed, resulting in varying degrees of injury.
What are the different types of spinal cord injuries?
Spinal cord injuries are classified into two main types: complete and incomplete. Complete injuries result in a total loss of motor and sensory function below the level of the injury, while incomplete injuries preserve some degree of function.
How do spinal cord injuries affect mobility?
Spinal cord injuries can significantly impact mobility, depending on the level and severity of the injury. Individuals with complete injuries may experience paralysis below the level of the injury, while those with incomplete injuries may have varying degrees of weakness or impaired coordination.
What are the long-term emotional effects of spinal cord injuries?
Spinal cord injuries can have a profound impact on an individual’s emotional well-being. Common emotional challenges include depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). These challenges can stem from the physical limitations, loss of independence, and social stigma associated with SCIs.
What resources are available for individuals with spinal cord injuries?
There are numerous resources available to support individuals with spinal cord injuries, including specialized medical care, rehabilitation services, support groups, and financial assistance programs. These resources aim to improve the quality of life for individuals with SCIs and help them achieve their full potential.