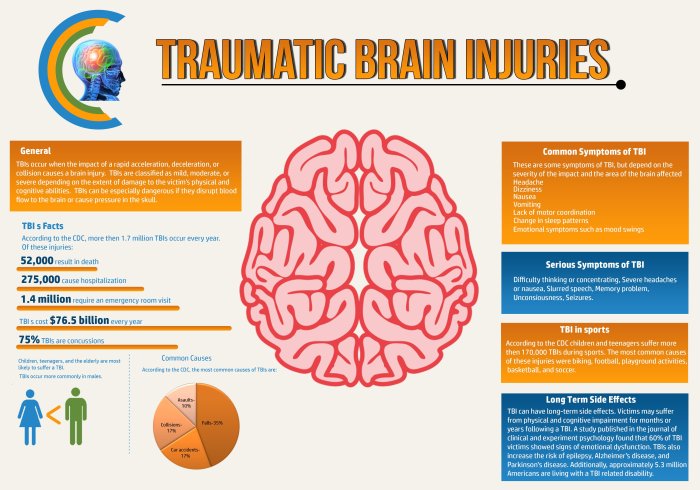
Traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) are a major public health concern, and car accidents are a leading cause of these injuries. TBIs can range in severity from mild to severe, and they can have a significant impact on a person’s life.
In this article, we will discuss the symptoms, treatment, and prevention of TBIs from car accidents.
TBIs can occur when the head is struck by a force, such as in a car accident. The force of the impact can cause the brain to move inside the skull, which can damage brain tissue. TBIs can also occur when the head is shaken violently, such as in a whiplash injury.
Symptoms of Traumatic Brain Injuries from Car Accidents
Traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) from car accidents can range from mild to severe, and their symptoms can vary widely. The severity and duration of symptoms depend on the extent of the injury, and they can significantly impact a person’s daily life.
Common Symptoms
The most common symptoms of TBIs from car accidents include:
- Headache
- Nausea or vomiting
- Dizziness or balance problems
- Confusion or disorientation
- Memory loss
- Difficulty concentrating
- Fatigue
- Sensitivity to light or noise
- Sleep problems
- Mood swings or irritability
Severity and Duration
The severity of TBI symptoms can range from mild to severe. Mild TBIs may cause symptoms that last for a few days or weeks, while moderate to severe TBIs can have symptoms that persist for months or even years.
Impact on Daily Life
The symptoms of TBI can significantly impact a person’s daily life. They can make it difficult to work, study, or perform other activities. TBIs can also lead to social isolation and relationship problems.
Treatment for Traumatic Brain Injuries from Car Accidents
Treatment for traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) from car accidents depends on the severity of the injury. Mild TBIs may only require rest and pain relievers, while more severe TBIs may require surgery, medication, and rehabilitation.
Types of Treatment Options
- Rest and pain relievers: Mild TBIs may only require rest and over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen.
- Surgery: More severe TBIs may require surgery to remove blood clots, repair skull fractures, or relieve pressure on the brain.
- Medication: Medications may be used to treat symptoms of TBI, such as seizures, headaches, and nausea.
- Rehabilitation: Rehabilitation is an important part of TBI treatment and may include physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy.
Benefits and Risks of Treatment Options
The benefits and risks of each treatment option for TBI vary depending on the severity of the injury.
- Rest and pain relievers: Rest and pain relievers are generally safe and effective for mild TBIs, but they may not be sufficient for more severe injuries.
- Surgery: Surgery can be life-saving for severe TBIs, but it also carries risks, such as infection, bleeding, and damage to the brain.
- Medication: Medications can be effective in treating symptoms of TBI, but they may also have side effects, such as drowsiness, dizziness, and nausea.
- Rehabilitation: Rehabilitation can help improve function and reduce disability after TBI, but it can be time-consuming and expensive.
Importance of Early Intervention and Rehabilitation
Early intervention and rehabilitation are essential for improving outcomes after TBI. Early intervention can help prevent complications and promote healing, while rehabilitation can help individuals regain function and improve their quality of life.
Diagnosis of Traumatic Brain Injuries from Car Accidents
Diagnosing traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) from car accidents involves a comprehensive approach that combines a thorough medical history, physical examination, and various diagnostic tools. Imaging tests, such as computed tomography (CT) scans and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), play a crucial role in identifying structural abnormalities in the brain.
Medical History and Physical Examination
A detailed medical history helps identify any pre-existing conditions or risk factors that may have contributed to the TBI. The physical examination assesses neurological function, including consciousness, memory, language, and motor skills. This helps determine the severity and location of the injury.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests provide detailed images of the brain to detect structural abnormalities caused by the TBI.
- CT Scans: CT scans use X-rays to create cross-sectional images of the brain. They are particularly useful for detecting skull fractures, bleeding, and other structural damage.
- MRI Scans: MRI scans use magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the brain. They can detect soft tissue injuries, such as contusions, swelling, and axonal damage, which may not be visible on CT scans.
These diagnostic tools, combined with a thorough medical history and physical examination, help healthcare professionals accurately diagnose TBIs from car accidents and determine the appropriate treatment plan.
Long-Term Effects of Traumatic Brain Injuries from Car Accidents
Traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) from car accidents can have long-lasting consequences that affect an individual’s cognitive function, behavior, and physical health. The severity and nature of these effects vary depending on the extent of the injury, but even mild TBIs can have significant long-term implications.
Cognitive Function
TBIs can impair cognitive abilities such as memory, attention, concentration, and problem-solving. Individuals may experience difficulty remembering recent events, paying attention to conversations, and making decisions. In severe cases, TBIs can lead to dementia or other cognitive impairments.
Behavior
TBIs can also affect an individual’s behavior. They may become more irritable, impulsive, or withdrawn. Changes in personality and mood are common, as are difficulties with social interactions.
Physical Health
TBIs can have physical consequences as well. They can increase the risk of seizures, headaches, and chronic pain. In severe cases, TBIs can lead to coma or even death.
Support and Resources
Individuals with long-term effects of TBIs can access a range of support and resources. These include:* Rehabilitation programs to help individuals regain lost skills and improve their quality of life
- Support groups to provide emotional support and a sense of community
- Financial assistance to cover the costs of medical care and other expenses
Final Summary
TBIs can have a significant impact on a person’s life. They can cause a variety of symptoms, including headaches, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and memory problems. In severe cases, TBIs can lead to coma or even death.
There is no cure for TBIs, but treatment can help to improve symptoms and prevent further damage to the brain. Treatment options for TBIs include medication, surgery, and rehabilitation. The type of treatment that is recommended will depend on the severity of the injury.
FAQ
What are the symptoms of a TBI?
The symptoms of a TBI can vary depending on the severity of the injury. Common symptoms include headaches, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and memory problems.
How is a TBI diagnosed?
A TBI is diagnosed based on a person’s symptoms and a physical examination. The doctor may also order imaging tests, such as a CT scan or MRI, to confirm the diagnosis.
What is the treatment for a TBI?
The treatment for a TBI depends on the severity of the injury. Treatment options include medication, surgery, and rehabilitation.
What are the long-term effects of a TBI?
The long-term effects of a TBI can vary depending on the severity of the injury. Some people may experience no long-term effects, while others may experience cognitive problems, behavioral problems, or physical problems.